Today, decentralized and traditional finance are moving past simply coexisting as they’re starting to overlap and influence each other. Because of this growing mix, it’s important to know the main characteristics of the two systems. In this article, we are going to explore and define the main differences between TrarFi and DeFi.
What Is Traditional Finance (TradFi) and How Does It Work?
Traditional finance is the long-standing financial system that includes central banks, commercial banks, and the infrastructure we use every day. Fiat currency as well as credit and debit cards, are all parts of the traditional financial system, also known as TradFi.
Traditional finance has a definitive structure and financial instruments that we are well familiar with. It relies on centralized entities and, while not fully transparent, it’s accepted as a trustworthy and main financial system.
What Is Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and How Does It Work?
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is a financial system based on blockchain technology. It removes banks and other middlemen from the picture and, instead of relying on institutions, DeFi uses smart contracts to handle things like lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest. Everything within DeFi runs on cryptocurrencies and digital assets, not traditional money.
Key Differences Between TradFi and DeFi
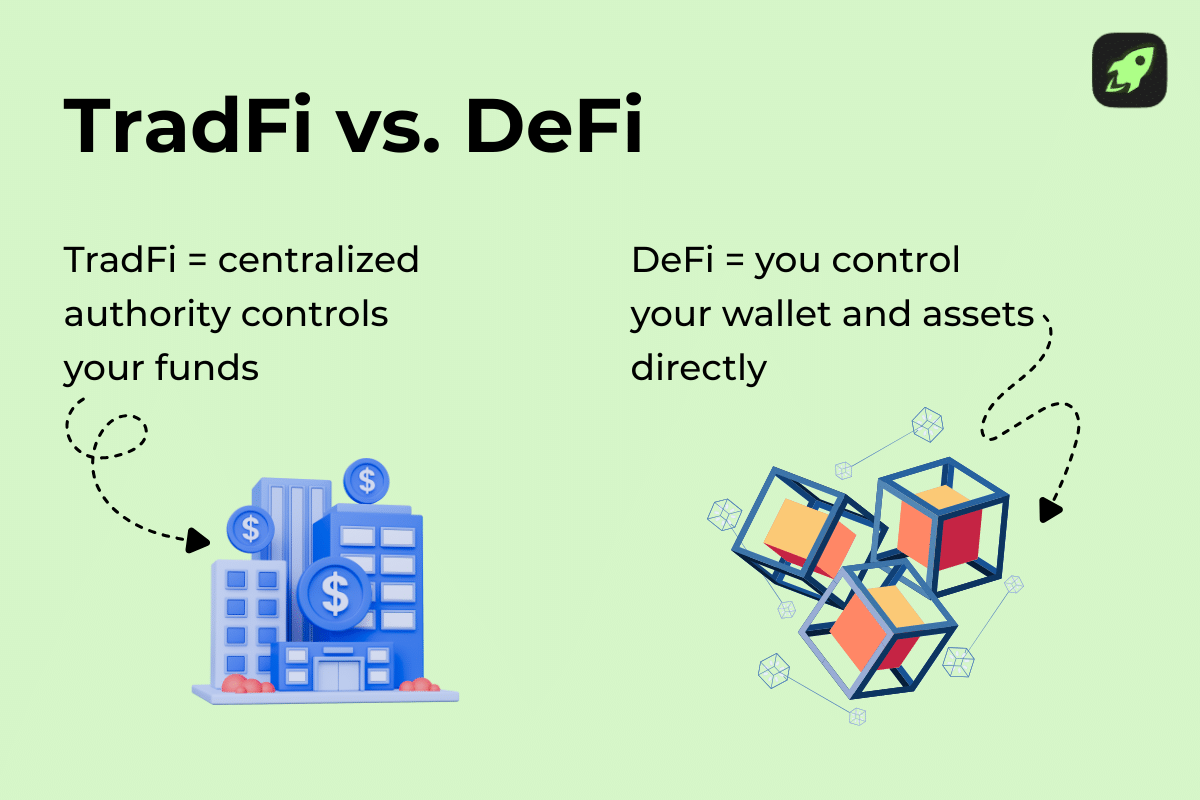
Traditional financial services and decentralized finance take completely different approaches to how money works. DeFi has no central authority — anyone with a wallet and an internet connection can access it. The system is fully transparent, since all financial transactions are recorded on public blockchains, and users keep control of their own funds. In TradFi, banks and institutions control your funds, act as intermediaries, and hold legal ownership of most financial assets. However, there are other differences that involve entry barriers, safety, regulations, and privacy in general.
DeFi vs TradFi: Key Differences Explained
To make the distinction between the finance systems clear, we would have to take a look at each point.
Control of Funds
In TradFi, banks and institutions control your money. When you deposit funds, you’re basically handing them over to be managed on your behalf. Banks can freeze accounts, reverse transactions, or impose limits whenever needed. DeFi flips this dynamic completely—you hold your funds in your own wallet, and only you can move them. There’s no bank to approve or deny anything. This gives you full independence but also full responsibility. Lose your private keys, send a transaction to the wrong address, or fall for a scam, and there’s no support line to fix it.
Ownership of Assets
TradFi gives you claims to assets, but not always true ownership. Stocks remain with a broker, money sits at a bank, and you mostly have access to both, but not direct control. DeFi gives you real, cryptographic ownership of assets stored in your wallet. If it’s in your address, it’s yours—simple as that. This eliminates custody risk but also removes the safety net institutions provide.

How to Get Free Crypto
Simple tricks to build a profitable portfolio at zero cost

Geographic Accessibility
Traditional finance is limited by geography and rules imposed by central banks. Banks operate within countries, payment systems vary by region, and many services require proof of residency. If you’re traveling or living in a restricted area, access is often limited. DeFi removes borders completely. As long as you have internet access and a crypto wallet, you can use DeFi apps from anywhere in the world.
Intermediaries
TradFi relies on intermediaries at every stage: banks, payment processors, brokers, clearinghouses, and regulators. These middlemen make the system more stable but also slower and more expensive. DeFi eliminates intermediaries by using smart contracts, which execute rules automatically. There’s no banker to sign off or broker to settle your trade—the code does it instantly. Once again, independence comes with risk. In DeFi, a buggy smart contract or poorly designed system can fail without anyone able to stop it.
Transaction Speed
Traditional financial transactions are notoriously slow. Bank transfers can take days, cross-border payments even longer, and securities sometimes take 2 or more days after reaching a solution to send the transaction. DeFi settles most transactions in seconds or minutes depending on the blockchain. This speed makes DeFi attractive for trading, lending, and real-time payments. Though, speed depends heavily on how ‘busy’ the network is—during high congestion, transactions can get stuck or become expensive. Still, compared to the traditional system, DeFi is lightning-fast.
Availability
Banks close, payment networks pause, and stock markets shut down every night and stay closed on weekends. TradFi availability depends on business hours and banking infrastructure. DeFi, on the other hand, never sleeps. It’s 24/7, global, and open every day of the year. You can send money, trade tokens, or borrow crypto at 3 AM on a Sunday without asking anyone for permission. This availability comes from decentralization—there’s no central server to turn off. The downside is that if something breaks or becomes congested, there’s no customer support team to fix it instantly.
Fee Structure
TradFi fees vary wildly. Banks can charge maintenance fees, withdrawal fees, wire fees, and even hidden fees buried in terms and conditions. DeFi fees depend mostly on blockchain gas costs and platform rules, making them more transparent. When the network is quiet, fees can be tiny, when it’s busy, they can spike. The structure is simpler but less predictable. Also, while TradFi fees pay for customer service, regulatory compliance, and security, DeFi fees mostly pay for blockchain miners/validators and smart contract operations, which changes how value flows in each system.
Cost Transparency
TradFi struggles with transparency. Banks or brokers rarely show you exactly how much you’re paying or why. Exchange spreads, hidden markups, and vague service fees add up quietly. DeFi aims for full transparency—you can see transaction fees upfront, inspect smart contracts, and verify all activity on-chain. Nothing is hidden because everything is public. But this doesn’t mean DeFi is always easy to understand. Gas fees can swing without warning, and some platforms still add service charges. Still, as a whole, DeFi makes it much clearer where your money is going.
Transparency
TradFi is largely opaque. Financial institutions don’t reveal how they manage risk, who they lend to, or how they operate internally. Decisions happen behind closed doors. DeFi is completely the opposite. Every transaction is publicly recorded on a blockchain. You can see smart contract code, track whale movements, and verify balances. This transparency builds trust without relying on institutions. It also means mistakes are visible to everyone, and scams can be traced publicly. Transparency doesn’t guarantee safety, but it removes the secrecy that often hides risk in traditional finance.
Consumer Protection
TradFi offers strong consumer protection: deposit insurance, fraud refunds, chargebacks, and legal recourse. If your card gets stolen or a bank error occurs, you’re usually covered. DeFi provides none of that. You’re your own bank—if you send funds to the wrong address, they are gone. You get no refunds after a hacker attack or if a project turns out to be a scam. DeFi users must rely on personal security, reading contracts, and community reputation. While some DeFi platforms add optional insurance or safeguards, the system as a whole lacks the safety nets most people are used to.
Regulations
TradFi is heavily regulated. Banks, brokers, and payment providers must follow strict rules, conduct audits, and operate under government oversight. This creates stability but slows innovation. DeFi exists mostly outside traditional regulation. Some jurisdictions set rules, but most DeFi apps operate globally with no central entity to regulate. This gives builders freedom to innovate rapidly but opens the door to scams, exploits, and risky behavior. Regulatory uncertainty will likely be eliminated over time, but for now, DeFi remains the “wild west” compared to traditional financial structures.
Security
TradFi relies on institutional security—encrypted databases, fraud monitoring systems, compliance teams, and insured deposits. It’s stable but targets large-scale breaches. DeFi uses cryptography and blockchain technology as its foundation. You secure your own funds with private keys, and smart contracts protect digital assets automatically. But smart contract bugs, hacks, and phishing attacks remain major risks. In short: TradFi security protects you through institutions; DeFi security depends on your tech knowledge and the quality of the code you trust.
Privacy of Transactions
TradFi monitors your activity closely. Financial institutions see every transaction, centralized entities can access your data, and identity verification is mandatory. DeFi offers more privacy—you interact through wallet addresses rather than personal identities. Transactions are public but not tied to your name unless you reveal it. This allows pseudonymity but not total anonymity. Privacy-focused users love this freedom, but regulators worry about misuse. New technologies like zero-knowledge proofs aim to balance transparency and privacy in the future.
Barriers to Entry
Conventional financial systems require IDs, proof of address, credit checks, and a decent financial history. People without documents or stable income are often excluded from using banking services and identity verification processes take days. DeFi removes almost all barriers. You need no ID, bank account, or any paperwork. Anyone with a smartphone and internet connection can participate. This makes DeFi powerful for global financial inclusion, but also opens doors to criminals, scams, and risky behaviors. The low barrier is both a strength and a challenge.
Yield Opportunities

TradFi offers predictable but limited yields, such as savings accounts, bonds, and dividends. DeFi offers high-yield opportunities through staking, lending, liquidity mining, and yield farming. Returns can be huge—but so can losses. High annual percentage rates often come with volatility, smart contract risk, and token inflation. TradFi yields are safer but smaller, DeFi yields are generous but risky. Choosing between them depends on your risk tolerance and experience.
Innovation Speed
TradFi changes slowly due to regulations, legacy systems, and risk management. New products take years to launch. DeFi evolves at lightning speed—new tools, tokens, and protocols appear every week. This rapid innovation drives creativity and growth but also increases risk. Some ideas break through and change the industry, others collapse overnight. DeFi is where experimentation happens first, and TradFi often follows years later.
H2 DeFi vs TradFi: Comparison Table
[Картинка таблицы сравнения]
| Category | TradFi (Traditional Finance) | DeFi (Decentralized Finance) |
| Control of Funds | Banks hold and control your funds. | You control your own wallet and funds. |
| Ownership of Assets | You have access, but institutions custody your assets. | Assets in your wallet = fully yours through cryptographic ownership. |
| Geographic Accessibility | Access depends on region, residency, and local rules. | Open to anyone worldwide with internet and a crypto wallet. |
| Intermediaries | Requires banks, brokers, processors, and clearinghouses. | Eliminates middlemen—smart contracts handle transactions. |
| Transaction Speed | Slow transfers; cross-border payments can take days. | Fast settlement within minutes or seconds depending on blockchain. |
| Availability | Limited by business hours, holidays, and banking infrastructure. | 24/7 access globally—no downtime, no closing hours. |
| Fee Structure | Complex, often with hidden or variable fees. | Fees are algorithmic and blockchain -based, though gas can fluctuate. |
| Cost Transparency | Low transparency; users often don’t know how fees are calculated. | High transparency—fees and smart contract logic are visible on-chain. |
| Transparency | Opaque operations and internal processes. | Fully transparent—every transaction recorded on a public ledger. |
| Consumer Protection | Strong protections: refunds, chargebacks, insurance. | No safety nets—mistakes, hacks, and scams are usually irreversible. |
| Regulations | Heavily regulated with strict regulatory oversight and compliance. | Lightly regulated and often global, creating a “wild west” environment. |
| Security | Institutional security systems + insured deposits. | Cryptographic security, but vulnerable to hacks and smart contract bugs. |
| Privacy of Transactions | Low privacy—banks track all activity and require identity verification. | Pseudonymous—wallet addresses replace personal identity. |
| Barriers to Entry | High barriers: ID checks, paperwork, stable income needed. | Low barriers: no ID or bank account required. |
| Yield Opportunities | Small but stable yields (savings, bonds). | High yields (staking, lending, yield farming) but with higher risk. |
| Innovation Speed | Slow—new products take years due to regulation. | Fast—new protocols, tokens, and tools appear constantly. |
Can DeFi and TradFi Work Together?
DeFi and TradFi might look like total opposites, but they’re slowly learning to work side by side. Centralized financial institutions are experimenting with blockchain technology for faster payments, and central bank digital currency, while DeFi platforms are adopting features like compliance tools, centralized exchanges, and safer onboarding. The two systems fill each other’s gaps too, as TradFi promises stronger financial stability, regulation, and consumer protection, while DeFi offers speed, global access, and constant innovation. Instead of choosing one over the other, the future will likely blend both.
Pros and Cons of TradFI
Traditional finance isn’t necessarily bad or good compared to DeFi, but here’s a list of the good and the bad it can offer.
Pros
- Strong consumer protection – refunds, insurance, and legal recourse available.
- Clear regulations – strict rules help prevent fraud and instability.
- Familiar systems – most people already understand how banking services work.
- Stable infrastructure – decades-old networks of financial institutions built for reliability.
- Lower personal responsibility – institutions safeguard funds for you.
- Widely accepted – usable everywhere for payments and transfers.
- Lower volatility – assets don’t swing wildly like crypto markets.
Cons
- Slow transactions – transfers can take days, especially cross-border.
- Limited access – requires IDs, paperwork, and compliant residency.
- High fees – hidden charges and service costs add up.
- Low transparency – operations happen behind closed doors.
- Centralized control – banks can freeze accounts or block transfers.
- Barriers to entry – some users excluded by credit or location.
- Less innovation – systems evolve slowly compared to crypto.
Pros and Cons of DeFi
Similarly, decentralized systems have their own better and worse elements that may affect your financial activities.
Pros of DeFi
- Full control of funds – you manage your crypto assets directly.
- Global accessibility – open to anyone with internet and a wallet.
- Fast cross border transactions – most operations settle within seconds or minutes.
- High transparency – everything is visible on public blockchains.
- Low entry barriers – no paperwork, credit checks, or bank accounts.
- High yield potential – staking and lending offer strong returns.
- Rapid innovation – new tools and ideas emerge constantly.
Cons of DeFi
- No consumer protections – mistakes or hacks usually aren’t reversible.
- Complex to learn – requires understanding wallets, fees, and risk.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities – bugs can cause major losses.
- Gas fees can spike – network congestion makes transactions expensive.
- Pseudonymous, not anonymous – transactions are public on-chain.
- Scams and rug pulls – unregulated space attracts bad actors.
- Self-custody risk – lose your keys, lose your assets forever.
When Should You Use DeFi or TradFi?
Choosing between DeFi and TradFi depends on what you need at the moment. If you want speed, global access, higher yields, or full control over your assets, DeFi is usually the better fit—especially for crypto-native activities like staking, swapping, or lending. But if you value stability, clear protections, predictable fees, and a human you can call when something goes wrong, the traditional financial system is still the safer choice. Most people end up using both: DeFi for flexibility and opportunity, TradFi for security and structure. The smartest approach is knowing when each system works in your favor.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, trusting DeFi or sticking to TradFi is every user’s personal choice. Both systems can offer something the other one lacks. DeFi is a more open financial system, while traditional banking remains the backbone of the economy. But even if you still don’t trust DeFi services, keep in mind that they are inevitably going to make their way into the everyday financial landscape. So it’s better to be prepared and know exactly what risks and advantages the system holds.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.